AWS: RDS vs DynamoDB – Choosing the Right Database for Your App
Posted On: July 12, 2025 | 2 min read
Choosing the right database is one of the most critical architectural decisions in any application. On AWS, two popular choices are Amazon RDS and Amazon DynamoDB. But how do you decide which one is right for you?
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service):
- Type: Relational (SQL-based) database service.
- Use Cases: Applications that need complex queries, relationships, and strict consistency (e.g., e-commerce, financial applications).
- Key Features:
- Supports popular engines like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQL Server.
- Automated backups, patching, and scaling.
- Strong ACID compliance.
Amazon DynamoDB:
- Type: NoSQL (key-value and document) database service.
- Use Cases: Applications requiring high-speed performance and scalability (e.g., gaming, IoT, real-time analytics).
- Key Features:
- Serverless, fully managed with automatic scaling.
- Single-digit millisecond latency.
- Flexible schema, great for unpredictable data models.
When to Choose Which?:
- RDS: Choose when you need relational integrity, complex joins, and transaction-heavy workloads.
- DynamoDB: Choose for massive scale, high-speed reads/writes, and when flexibility is more important than strict relational rules.
Quick Diagram (Conceptual):
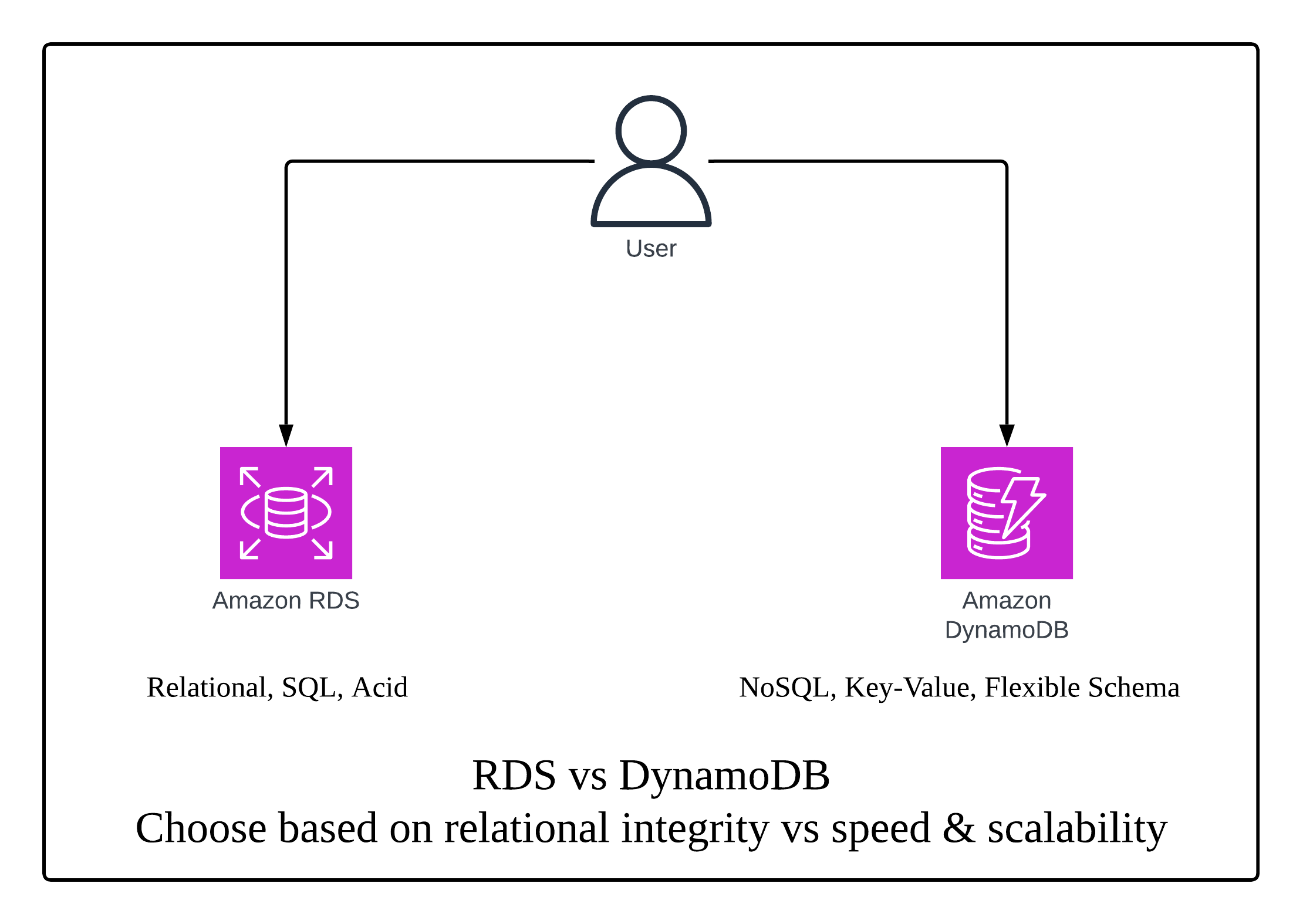
RDS vs DynamoDB – Choose based on relational integrity vs speed & scalability
Conclusion:
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. If your application heavily relies on structured relationships and transactions, RDS is your go-to. For highly scalable, low-latency workloads, DynamoDB is the better fit.
Link copied!
Comments
Add Your Comment
Comment Added!


No comments yet. Be the first to comment!