Data Insights: Introduction to Apache Kafka for Data Streaming
Introduction
In today’s digital world, businesses generate and consume data at incredible speeds — from financial transactions and e-commerce clicks to IoT sensor readings. Handling this real-time data requires more than traditional databases or batch systems. This is where Apache Kafka comes in.
Originally developed at LinkedIn, Kafka has become the industry standard for distributed data streaming, powering applications at companies like Netflix, Uber, and Airbnb.
What is Apache Kafka?
Apache Kafka is a distributed event streaming platform designed for:
- Publishing and subscribing to event streams (like a messaging system).
- Storing streams of events reliably.
- Processing streams of events in real time.
In simple terms: Kafka moves data between systems quickly and reliably.
Core Concepts
- Producer
- Applications that publish events to Kafka (e.g., user clicks, transactions).
- Topic
- A category or stream name to which records are sent (like “orders” or “logs”).
- Consumer
- Applications that subscribe and read events from topics.
- Broker
- A Kafka server that stores data and serves clients. Multiple brokers form a cluster.
- Partitions
- Topics are split into partitions for scalability and parallel processing.
- ZooKeeper (legacy) / KRaft (new)
- Used for managing cluster metadata (KRaft is replacing ZooKeeper).
Apache Kafka Architecture Diagram
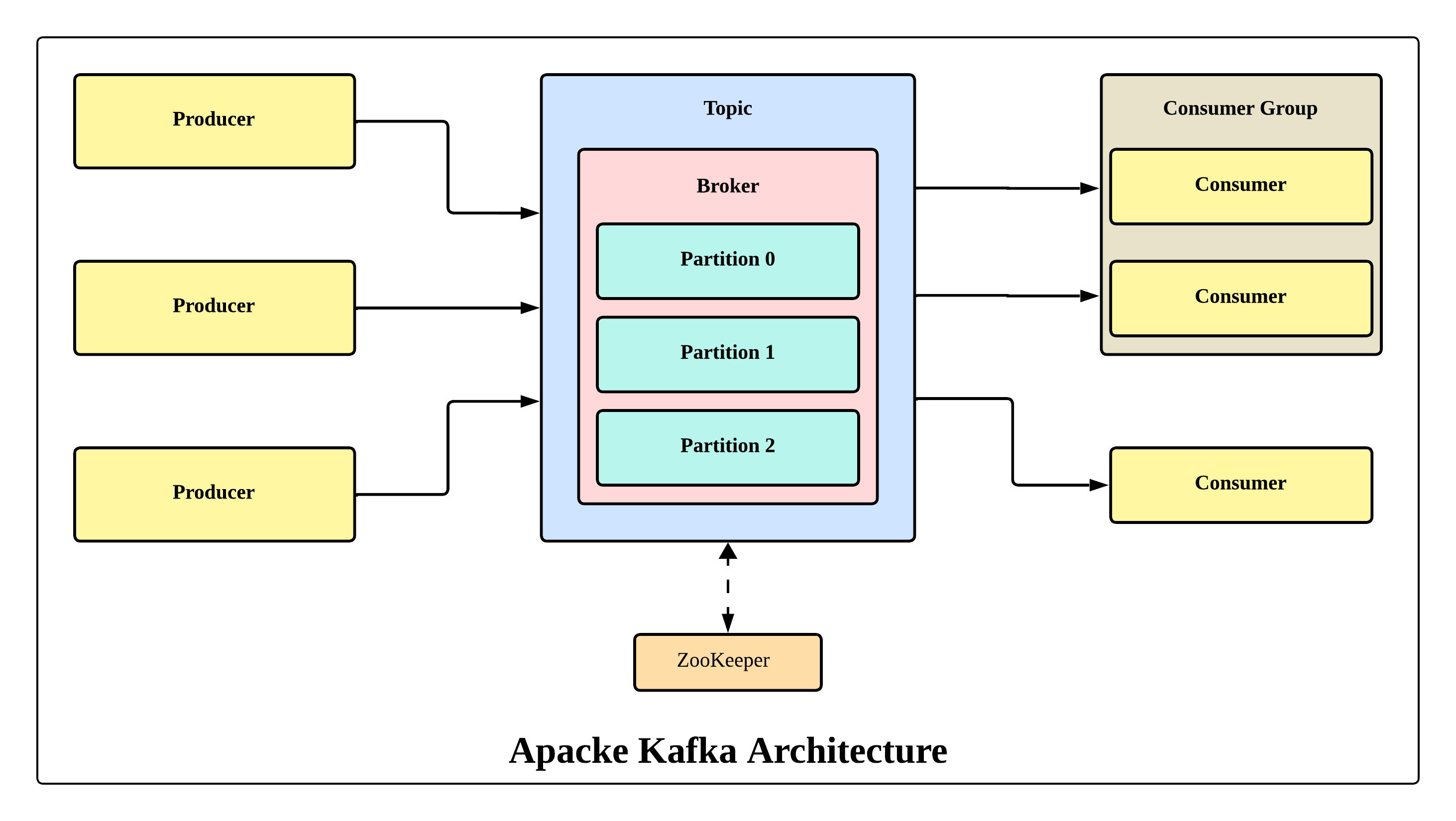
Figure: Apache Kafka Architecture
Why Use Kafka?
- Scalability → Handle millions of messages per second.
- Durability → Stores events on disk, replicated across brokers.
- Performance → High-throughput, low-latency data pipelines.
- Flexibility → Integrates with databases, stream processors, and analytics tools.
Common Use Cases
- Real-Time Analytics → Website clickstream analysis, fraud detection.
- Log Aggregation → Collect logs from multiple services for monitoring.
- Event-Driven Systems → Microservices communication via events.
- IoT Data Streaming → Processing sensor data in real time.
- Data Integration → As a central backbone for moving data across systems.
Pro Tip
Kafka is not a database replacement. Use it for event streaming and data pipelines, then connect it to storage systems (like S3, Hadoop, or relational DBs) for long-term analysis.
Takeaway
Apache Kafka has become a cornerstone of modern data infrastructure. By enabling real-time event streaming, it powers use cases from fraud detection to IoT. For businesses dealing with continuous streams of data, Kafka isn’t just a nice-to-have — it’s a critical enabler of speed, scalability, and reliability.





No comments yet. Be the first to comment!